A 5-carbon sugar a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. DNA is present as the genetic material in all the living organisms except some viruses.
Two types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA.
What is nucleic acids monomer. Monomers are monosaccharides simple sugars. Additionally what are the 3 key roles of DNA. A molecule found in DNA and RNA that encodes genetic information in cells.
Monomers are the building blocks that make up nucleic acid. The monomers that make up nucleic acids are called nucleotides which composed of three parts. 3 Show answers Another question on Biology.
It plays a key factor in transferring genetic information from one generation to the next. Monomer of Nucleic Acids Nucleotides are the individual monomers of a nucleic acid. Nucleic acids can be defined as organic molecules present in living cells.
There are two types of nucleic acids-Ribonucleic acid RNA and Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA Ribonucleotides are monomers of RNA and Deoxyribonucleotides are monomers of DNA. The monomer of nucleic acid. Carbohydrates - polymers are polysaccharides and disaccharides.
DNA is made of the polymers of nucleotides. What are the monomers that build this polymer. Obviously the monomer of nucleic acid is a single unit of nucleotide.
Nucleic Acid Monomer Nucleotide Phosphate Group. All types of monomers are organic molecules which means that they consist of carbon-to-carbon bonds. What is the full name of DNA.
Name and describe the various RNA molecules found in the cell. When it comes to nucleic acids its basic unit or monomer is the nucleotide. The monomer or the repeating unit is known as the nucleotides and hence sometimes nucleic acids are referred to as polynucleotides.
A common example of this is ATP which stores energy. One gene can influence traits. Nucleic acids are long-chain polymeric molecules.
What helps you tell easily that this is a nucleotide present in DNA but not in RNA. How does it differ from DNA. When free these monomers may have extra phosphate groups and be found in diphosphate triphosphate or polyphosphate forms.
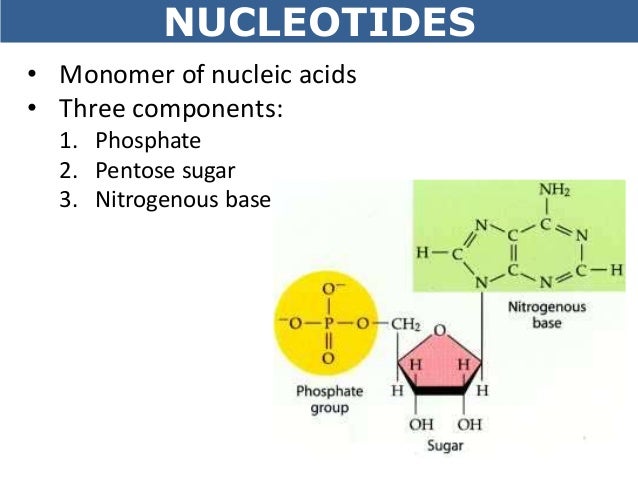
DNA is a nucleic acid polymer. What is the monomer unit of a Nucleic Acid. The three groups are a Phosphate Group a Pentose Sugar five-sided or five-carbon sugar and a Nitrogen Base.
The three main functions of DNA are as follows. The nucleic acid is a long chain of nucleotides known as polynucleotide chain which encodes a particular protein. What is the 77 element on the periodtic table.
Why is DNA important. The monomer units of DNA are nucleotides and the polymer is known as a polynucleotide Each nucleotide consists of a 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose a nitrogen containing base attached to the sugar and a phosphate group. Each nucleotide is composed of three parts.
RNA is present as genetic material in some viruses only. A ribonucleotide monomer is composed a nitrogenous base purine or pyrimidine a ribose sugar and a phosphate group. The monomers of nucleic acid are called nucleotides.
5 What are the monomers of Carbohydrate lipids proteins. One trait can. Nucleotide monomers are named according to the type of nitrogenous base they contain.
Monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Nucleic acids aka DNA and RNA are composed out of monomer units called nucleotides. These molecules are fairly complex consisting of a nitrogenous base plus a sugar-phosphate backbone There are four basic types of nucleotide adenine A guanine G cytosine C and thymine T.
Nucleic acids are polynucleotidesthat is long chainlike molecules composed of a series of nearly identical building blocks called nucleotides. Nucleic acids are polymers of individual nucleotide monomers. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA two molecules essential for life as we know it.
Molecules of both DNA and RNA serve as the genetic code that uniquely identifies every living organism. Monomers are nucleotides which are in turn consist of a nitrogenous base pentose sugar and phosphate group. Nucleic Acids - polymers are DNA and RNA.
What are the three parts to a nucleotide. Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogen-containing aromatic base attached to a pentose five-carbon sugar which is in turn attached to a phosphate group. To breakdown the structure of a nucleotide it is composed of a nucleoside a derivative of purine or pyrimidine that has a sugar molecule linked to the nitrogen ring with a phosphoryl group esterified to the hydroxyl.
Some nucleotides conduct vital cellular functions by functioning as an independent molecule. Nucleic Acid Monomers The chemical formulas of nucleic acid monomer show the quantities of each element. Only two 5-carbon sugars are found in nature.
Mono- one mer- part A sugar nitrogenous base and phosphate are collectively called as a nucleotide. Monomers bind to another monomer to form a chain of molecules in a process called polymerization. Also known as nucleotides they are composed of a five-carbon sugar a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.
A strong acid or strong base completely dissociates eg HCl or NaOH while a weak acid or weak base only partially dissociates eg acetic acid. Because MgOH 2 is listed in Table 122 Strong Acids and Bases it is a strong base.
 Weak Acid Base And Their Conjugate Base Acid In Buffer Solutions Download Table
Weak Acid Base And Their Conjugate Base Acid In Buffer Solutions Download Table
Many acids and bases are weak.

Weak acids and bases. If so or if not so please give some explanations on the possible reasoning using their structures. A weak acid is one that does not dissociate completely in solution. Also I have another question which is quite related but too short to be posted as an independent question so I will ask here.
Weak acids and bases are only partially ionized in their solutions whereas strong acids and bases are completely ionized when dissolved in water. All strong acids behave the same in water1 M solutions of the strong acids all behave as 1 M solutions of the H3O ionand very weak acids may not act as acids in water. Our generic reactions for a weak acid HA and a weak base B in water are the following.
Notice that these are both ionizationsThe fact that they are playing the role of a weak acid and a weak base also means that the forward reaction only proceeds by 1. Weak Acids and Bases. Most weak bases are anions of weak acids.
HO 2 CCH 3 HCl HO 2 CCH 3 Cl. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The nitrogen in C 5 H 5 N would act as a proton acceptor and therefore can be considered a base but because it does not.
HAaq H 2 O. H 3 PO 4. All the other acids are weak.
Today chemists can also use pH indicator paper which turns every color of the rainbow to indicate how strong or weak an acid or base is. Weak bases do not furnish OH - ions by dissociation. In a strong acid the acid molecules are completely ionised.
Organic acid carboxylic acid - an acid except carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 aq containing carbon oxygen and hydrogen atomsAn organic acid has a carbon backbone and a carboxyl group -COOH. Because HCl is listed in Table 122 Strong Acids and Bases it is a strong acid. HA S A HS.
There are only a few 7 strong acids so many people choose to memorize them. The Ionization of Weak Acids and Weak Bases. Polyprotic bases take more than one proton from water and also have more than one ionization constant K b1 K b2 etc.
A weak acid is one that does not dissociate completely in solution while a weak base is a chemical base that does not ionize fully in an aqueous solution. State with two examples on each how a strong and weak acidbase relate to its conjugate acidbase pairs. This means that a weak acid does not donate all of its hydrogen ions H in a solution.
Strong and weak bases - definition Weak bases are only partially ionized in their solutions whereas strong bases are completely ionized when dissolved in water. Diethylamine CH 3 CH 2 2 NH. Like weak acids weak bases do not completely dissociate in aqueous solution.
Strong and Weak Acids and Bases The strength of acids and bases depends on their ability to dissociate or break into their ions in water. Polyprotic acids have more than one proton to donate to water and so they have more than one ionization constant K a1 K a2 etc that can be considered. Some common weak acids and bases are given here.
A chemical patch turned red for acids blue for bases. According to BronstedLowry acidbase theory the solvent S can accept a proton. For example hydrochloric acid is a weak acid in solution in pure acetic acid HO 2 CCH 3 which is more acidic than water.
Baq H 2 O. Most organic acids are weak acids. Ethanoic acid is an example of a weak acid.
Identify each acid or base as strong or weak. One of the earliest tests to determine acids from bases was the litmus test. The percent dissociation of a weak acid is the fraction of acid molecules that dissociate compared with the initial concentration of the acid.
The strong acids are hydrochloric acid nitric acid sulfuric acid hydrobromic acid hydroiodic acid perchloric acid and chloric acid. BH aq OH aq. CH 3 NH 2.
Acids react with bases to give salt and water only. That is they do not ionize fully in aqueous solution. Only aqueous solution of acids have acidic properties.
A chemical patch turned red for acids blue for bases. Instead they react with water to generate OH - ions. Examples of strong base are N a O H K O H Examples of weak bases are N H 3 N a 2 C O 3.
H 2 CO 3. Acids have a sour taste. 88n NH3 H2O Weak acid Bronsted Acids and Bases in Nonaqueous Solutions Water has a limiting effect on the strength of acids and bases.
Is there any substance that acts as a weak acid and a strong bases at the same time or vice versa. Furthermore weak acids and bases are very common and we encounter them often both in the academic problems and in everyday life. Weak Polyprotic Acids and Bases.
Acidbase reactions dont have to occur in water however. Sulphuric acid is an example of a strong acid which is found. Examples of weak bases include ammonia NH 3 and diethylamine CH 3 CH 2 2 NH.
Start studying Strong and weak acids and bases. The only weak acid formed by the reaction between hydrogen and a halogen is hydrofluoric acid HF. A solution of a weak acid in water is a mixture of the nonionized acid hydronium ion and the conjugate base of the acid with the nonionized acid present in the greatest concentration.
H 3 O aq A aq. An acid which is strong in water may be weak in a less basic solvent and an acid which is weak in water may be strong in a more basic solvent. Acids are compounds that can donate protons upon dissolving them in.
Weak Acids and Bases. MgOH 2 C 5 H 5 N.
Imino acids are related to amino acids which contain both amino -NH 2 and carboxyl -COOH functional groups differing in the bonding to the nitrogen. Because the COOH functional group is an acid and the NH 2 functional group is a base the two ends of amino acids can readily react with each other.
 Amino Acid Definition Structure Facts Britannica
Amino Acid Definition Structure Facts Britannica
What is the effect of excess heat or temperature on an enzyme.
Name the 2 functional groups in amino acids. Because the carboxyl group is an acid it can form peptide bonds with the base amino groups of other amino acids causing chemical reactions that create polypeptide chains and amino acid residues. ExplanationTHE NAMES OF FUNCTIONAL GROUP OF AMINO ACIDS - - 1 NH2 2 COOH 1. As the name implies amino acids contain an amine and a carboxylic acid functional group.
Also the direct biosynthetic precursor to the amino acid proline is the imino acid S-D 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate P5C. Names include prefix. These functional groups dominate their physical and chemical properties.
Name the 2 functional groups in amino acids. Lysine arginine and histidine are amino acids which have simple side chains. A functional group containing two carbonyls separated by an oxygen atom.
The amino and carboxyl ends of the two amino acids come together and the nitrogen of the amino group bonds with the carbon on the carboxyl group. The D-amino acid oxidase enzymes are able to convert amino acids into imino acids. 50 points Name the 2 functional group in amino acids Ask for details.
Follow Report by Nathanielloughner 23082019 Log in to add a comment. In an aqueous solution at physiological pH all three functional groups on these amino acids will ionize thus giving an overall charge of 1. Aspartic and glutamic are the two acidic amino acids.
Enzymes have an attachment site called the _____ site for the _____ to join. Amino acids are of different types eg. A carboxyl group COOH is a functional group consisting of a carbonyl group CO with a hydroxyl group O-H attached to the same carbon atom.
Posted on February 7 2019 February 22 2019 by Katherine Sales Posted in Amino Acids Health Tagged Amino Acids functional groups molecular formula negatively charged nonpolar side polar side positively charged single letter code Three 3 letter code. Where there is an amine functional group in the side chain the amino acid creates a basic solution so the acid group does not neutralise the additional amine group. The amino group consists of one nitrogen atom and two hydrogen atoms.
Acidicbasicneutral imino and sulpher containing etc but all types of amino acids possess two functional groups. Amino acids are of different types eg. Amino- or the suffix amine.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games. Each has a carboxylic acid on its side chain that gives it acidic proton-donating properties. Amino Acids- A functional Group.
The carboxyl and amino group. These groups are joined to a single aliphatic carbon. Amino acids as the name implies have two functional groups an amino group NH 2 and a carboxyl group COOH.
The key chemical characteristic of amino acids is that they link together to form proteins. Amino acids are a group of organic compounds containing two functional groups- amino and carboxyl. Amino acids and their functional groups are a must for health and survival.
The carboxyl and amino groups lie at opposite ends of an amino acid. The amino group is NH 2 but under acidic conditions it gains a proton and becomes NH 3. Name The Two Functional Groups Are Included In Every Amino Acid And Are Necessary For Amino Acids To Join Together To Form A Polypeptide.
These functional groups are amino group. Amino acids are classified according to the relative position of the functional groups. Under neutral conditions pH 7 the amino group of an amino acid carries the 1 charge giving.
The two amino acids in this group are aspartic acid and glutamic acid. There are also guidelines for the non-essential amino acids cysteine 19 mgkg and tyrosine 33 mgkg. The amino group -NH2 is basic while the carboxyl group COOH is acidic in nature.
Carboxyl groups have the formula -COOH usually written as -COOH or CO 2 H. There are over 700 naturally occurring amino acids. Acidicbasicneutral imino and sulpher containing etc but all types of amino acids possess two functional groups.
The amino functional group is a basic or alkaline group. Carboxylic acids are a class of molecules which are characterized by the presence of one carboxyl group. In organic chemistry the carbon directly attached to a carboxyl group is the alpha a position so the amino acids in proteins are all alphaamino acids.
When two amino acids react and form a peptide bond and that process goes on to be repeated many amino acids may string together which forms a protein structure. Identify Each Of The Following Amino Acids By Name And Single Letter Abbreviation COO COO COO COO H2N-CH H3N-CH H3NCH H3N-CH 1 CH2 CH2 CH2 HC CH2 CH2 CH CH2 CH2 H3C CH3 OH CH2 NH3 D A B s 3. Cells have _____ of enzymes to act as biological _____ thousands catalysts.
Its commonly seen in amino acids proteins and the nitrogenous bases used to build DNA and RNA. The general structure of amino acids The amino acids are termed as a-amino acids. All of your bodies essential amino acid needs can be met by having a healthy balanced dietHowever there are some advocates for taking high concentration supplements to improve factors such as mood sleep exercise performance weight loss and prevent muscle loss.
Start studying Functional Groups and Amino Acids. Two amino acids form a peptide or amide bond when they join. Protein synthesis is more complicated than a simple acid-base neutralization but consider what happens when two amino.
Aldehydes RCHO.