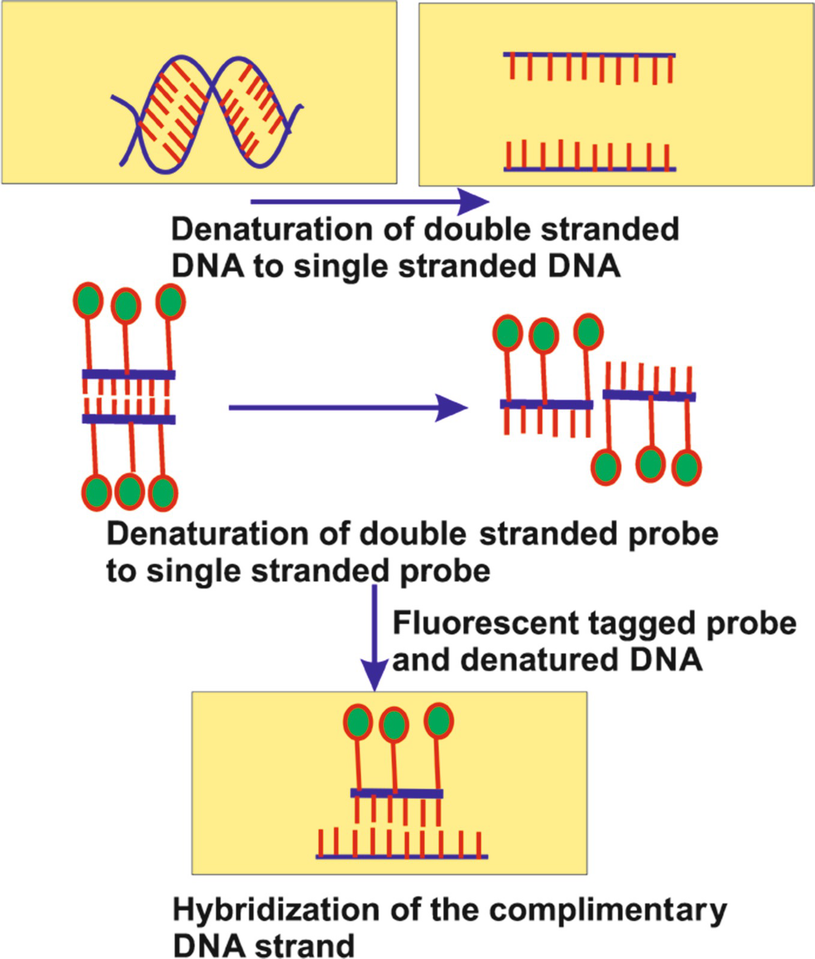
The DNA probe typically comes from cloned sources such as plasmids cosmids PACs YACs or BACs. Fluorescence in situ hybridization is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only those parts of a nucleic acid sequence with a high degree of sequence complementarity.
 Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization Fish Using Pas1 Red Psc119 2 Download Scientific Diagram
Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization Fish Using Pas1 Red Psc119 2 Download Scientific Diagram
Its used to localize particular DNA sequences or lack thereof on a chromosome in order to detect chromosomal abnormalities or mutations.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization. Like deletion duplication or translocation of a DNA segment. Twenty cutaneous melanomas and 20 cutaneous nevi from pathology files were selected and. The DNA probe and the target DNA to which the probe will be hybridized.
The Fluorescence In-Situ Hybridization Fish market report focuses on. A team of scientists from France has recently designed fluorescence in situ hybridization probes CoronaFISH to visualize severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 SARS-CoV-2 RNA in. This may be used for understanding a variety of chromosomal abnormalities and other genetic mutations.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization FISH is a kind of cytogenetic technique which uses fluorescent probes binding parts of the chromosome to show a high degree of sequence complementarity. Where the insert may contain a specific gene or originate from a specific chromosomal. Fluorescence in situ hybridization is a cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent DNA segments called probes to bind to a known DNA sequence.
The DNA is labeled with a fluorescent dye and hybridized to a cytological preparation of chromosomes that has been denatured to allow nucleic acid hybridization between chromosomal DNA and the probe. Fluorescence in situ hybridization FISH is a laboratory technique for detecting and locating a specific DNA sequence on a chromosome. Definition In situ hybridization is the method of localizing detecting specific nucleotide sequences in morphologically preserved tissue sections or cell preparations by hybridizing the complementary strand of a nucleotide probe against the sequence of interest.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization FISH is a laboratory technique for detecting and locating a specific DNA sequence on a chromosome. Fluorescence microscopy can be used to find out where the fluorescent probe bound to the chromosome. It was developed by biomedical researchers in the early 1980s to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes.
The technique relies on exposing chromosomes to a small DNA sequence called a probe that has a fluorescent molecule attached to it. A method for locating a segment of DNA on a chromosome. The fluorescent probes are nucleic acid labeled with fluorescent groups and can bind to specific DNARNA sequences.
Molecular medicine Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization. Multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization FISH in its simplest form can be used to identify as many labeled features as there are different fluorophores used in the hybridizationBy using not only single colors but also combinations of colors many more labeled features. Using spectrally distinct fluorophore labels for each hybridization probe this approach gives you the power to resolve several genetic elements or multiple gene expression patterns through multicolor visual display.
One of them is the comparative genomic hybridization. Which may be the underlying cause of. The fluorescence in situ hybridization technique is capable of detecting larger copy number variation efficiently.
CGH used for quantitative detection of copy number variations. Multiplex fluorescence in situ hybridization FISH enables you to assay multiple targets and visualize colocalized signals in a single specimen. FISH is often used for finding specifi.
This latest report studies Fluorescence In-Situ Hybridization Fish market 2020 research report is replete with precise analysis from radical studies specifically on queries that approach Market size trends share forecast outlook production and futuristic developments trends and present and future market status. The power of in situ hybridization can be greatly extended by the simultaneous use of multiple fluorescent colors. The probe sequence binds to its corresponding sequence on the chromosome.
Fluorescence microscopy can be used to find out where the fluorescent probe is bound to the chromosomes. Developed in the 1980s FISH is used for examining the cellular reproduction cycle specifically during interphase to identify chromosomal abnormalities. Fluorescence in situ hybridization FISH is a molecular cytogenetic technique that has revolutionized the way chromosomes are examined 7.
The technique relies on exposing chromosomes to a small DNA sequence called a probe that has a fluorescent molecule attached to it. Fluorescence in situ hybridization FISH provides researchers with a way to visualize and map the genetic material in an individuals cells including specific genes or portions of genes. ContextRecent advances in understanding the molecular basis of melanoma have resulted in development of fluorescence in situ hybridization FISH protocols designed to detect.
Fluorescence in situ Hybridization FISH involves the preparation of two main components. To explore the utility of fluorescence in situ hybridization as a diagnostic tool for cutaneous melanoma. Fluorescence in situ hybridization FISH is a technique that uses fluorescent probes which bind to special sites of the chromosome with a high degree of sequence complementarity to the probes.
In situ hybridization ISH is a type of hybridization that uses a labeled complementary DNA RNA or modified nucleic acids strand ie probe to localize a specific DNA or RNA sequence in a portion or section of tissue or if the tissue is small enough eg plant seeds Drosophila embryos in the entire tissue whole mount ISH in cells and in circulating tumor cells CTCs. Scientists are now applying different variations of FISH for different cytogenetic applications.