I dont know exactly what non-specific means medically but vertigo. General symptoms seen with all non-specific brain lesions include.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-these-spots-on-my-mri-2488902-5c5db0fa46e0fb0001ca86cb.png) Spots On An Mri White Matter Hyperintensities
Spots On An Mri White Matter Hyperintensities
The headache associated with brain lesions appears out of the blue.

Non specific brain lesions. Brain lesions induced by specific and non-specific inhibitors of sodium-potassium ATPase. 03 6166 0000 Fax. The non-specific symptoms of brain lesions include.
Often a brain lesion has a characteristic appearance that will help your doctor determine its cause. Non-specific is used for a symptom sign test result radiological finding etc that does not point towards a specific diagnosis or etiology. Specific brain lesions cause specific symptoms such as dyskinesias and altered movements in Parkinsons disease and dementia memory.
The radiologist report from several MRIs say that the lesions in my brain are possibly early demyelinating disease versus ischemic but most of the neuros Ive seen all say that the brain lesions are non specific. Dizziness were my first MS symptoms. There are several causes of white spots on a brain MRI including small strokes migraines multiple sclerosis MS lupus B12 deficiency a brain tumor such as lymphoma or an infection such as Lyme disease or HIV.
An unexplained headache is perhaps the most common and the first to appear symptom in brain lesions. Sometimes lesions appear in a specific area of the brain. Neck pain and stiffness.
From my MRI they could see that I had a lesion in a part of my brain that would cause dizziness. Among the known possible causes of brain lesions are. Brain MRI had non specif lesions and the other part of the spines MRI was free of lesions.
View on a map. Brain abscesses are areas of infection including pus and inflamed tissue. On CT or MRI scans brain lesions appear as dark or light spots that dont look like normal brain tissue.
I will have an MRI for the rest of the spine as we read more. Im not clear on the meaning of non specific or whether a neuro can eventually use them as evidence as a disease process occurring. I had a brain and a spinal cord MRI only cerebral part.
Specific lesion types might indicate a flare-up or reveal damage occurring in the brain. Sometimes the cause of the abnormal-appearing area cannot be diagnosed by the image alone and additional or follow-up tests may be necessary. It is a good idea to have regular scans so that a doctor can assess the progression of the disease.
Non specific lesion on MRI. Basspro22 Hello everyone I went to the Dr because I was having some unexplained muscle twitching in right left arm and randomly throughout different parts of the body at times. Non-specific is a widely-used term in radiology and clinical medicine in general.
Brain lesions are a type of damage to any part of brain. A patient may have predominantly spinal MS in which case the brain may be largely spared of lesions whereas spinal cord MRI contains peripherally placed short-segment intramedullary lesions typical of demyelination. They are not common but they are life threatening.
A brain lesion is an abnormality seen on a brain-imaging test such as magnetic resonance imaging MRI or computerized tomography CT. Altered gait and posture. Lees GJ1 Leong W.
Wellington Clinics Level 10 42 Argyle Street Hobart Tas 7000. 1Department of Psychiatry and Behavioural Science School of Medicine University of Auckland New Zealand. At other times the lesions are present in a large part of the brain tissue.
6 Another rare scenario is a patient with a history of a classic MS-like relapse eg optic neuritis or brainstem syndrome in whom a lesion may have resolved on subsequent MRIs. That was not enough for them to diagnose MS so they did an MRI of my spinal column and saw another lesion. Lesions on the brain is a phrase that many people use to find information about brain problems.
What are brain lesions. Initial signs and symptoms of a brain lesion are often non-specific and may include. For example a high T2 signal lesion of the white matter on an MRI brain is a non-specific finding as the number of.
Professor Hedley Emsley explains what white matter lesions are the range of potential causes if they can cause problems and more. Fever if an infection is present Neck pain and stiffness if the meninges are inflamed Affected vision if there is damage along the pathway from the optic nerve to the occiput. Here are some common brain lesions.
Lesions can be due to disease trauma or a birth defect. At first brain lesions may not produce any symptoms. The phrase is non-specific and indicates that the searcher may desire an introduction to this vast highly detailed and complicated subject.
Disruption of the basal ganglia network forms the basis for several movement disorders eg Parkinsons Disease Huntington Disease. They form a part of the extrapyramidal motor system and work in tandem with the pyramidal and limbic systems.
 Basal Ganglia Direct And Indirect Pathway Of Movement Osmosis
Basal Ganglia Direct And Indirect Pathway Of Movement Osmosis
Each part of the basal ganglia plays its own separate role in the brain but they also form a network with each other.

Where is basal ganglia located in the brain. Basal ganglia are structures located in the base of the forebrain. Neurons are brain cells that act as messengers by sending signals throughout the nervous system. The basal ganglia consist of the corpus striatum a major group of basal ganglia nuclei and related nuclei.
The right basal ganglia located in the cerebrum is responsible for movement control and dopamine production. They are significantly united with the cerebral cortex thalamus and brainstem. Being in the brain its part of the central nervous system.
Basal ganglia originates from the telencephalon forebrain and is developmentally related to the cerebral cortex amygdala olfactory and hippocampal formation. The basal ganglia are located in the inferior lower-est or underneath portion of the brain. The right basal ganglia is the right half of the collection brain nuclei that is responsible for movement control and dopamine production.
The basal ganglia or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical structures found deep within the white matter of the brain. Basal ganglia group of nuclei clusters of neurons in the brain that are located deep beneath the cerebral cortex the highly convoluted outer layer of the brain. Updated July 24 2019 The basal ganglia are a group of neurons also called nuclei located deep within the cerebral hemispheres of the brain.
Their most important roles are to orchestrate movement regulate feelings of reward and govern other instinctual needs. The structures generally included in the basal ganglia are the caudate putamen and globus pallidus in the cerebrum the substantia nigra in the midbrain and the subthalamic nucleus in the diencephalon. What is Basal Ganglia.
The basal ganglia or basal nuclei are group of subcortical nuclei located at the base of the forebrain. Each part of the basal ganglia reside in the white matter of the cerebral cortex. We will try to untangle the mystery a bit in order to understand the crucial function they play.
It consists of the striatum pallidium substanta nigra and the subthalamic nucleus. Unlike the other ganglia mentioned above its not part of the peripheral nervous system. The basal ganglia play a major role in voluntary motor functions procedural learning routines or habits and eye movements.
The basal ganglia are situated at the base of the forebrain and top of the midbrain. The basal ganglia are a group of specialized brain cells located deep in the middle of the brain. The basal ganglia is located in the brain.
Where you should exercise caution however is with the term ganglia Ganglia is said to be a bit of a misnomer in that this term refers to an assemblage of neurons specifically in the peripheral nervous system. The basal ganglia are located at the base of the forebrain cerebrum and have attracted attention in medicine for various disturbances that appear with dysfunctions caused by diseases or trauma. The basal ganglia are neurons deep in the brain that are key to movement perception and judgment.
What are the Basal Ganglia. This structure important in regulating voluntary movements. The basal ganglia are a set of brain structures located beneath the cerebral cortex that receive information from the cortex transmit it to the motor centers and return it to the part of the cerebral cortex that is in charge of motion planning.
The structures that make up the basal ganglia include the. Basal ganglia are strongly interconnected with the cerebral cortex thalamus and brainstem as well as several other brain areas. The basal ganglia are a group of structures found deep within the cerebral hemispheres.
Basal ganglia within red square. Located in the middle part of the brain the basal ganglia is the area of the brain that is responsible for a great deal of motor control and learningThis area works in conjunction with the cerebral cortex and the thalamus to help us make decisions and shift between activities. MeSH Also referred to as paleostriatum Substantia Nigra.
The basal ganglia are a group of structures found deep within the base of the brain. The basal ganglia represent a. The basal ganglia are involved primarily in processing movement-related information.
There is a lot of confusion and complex terminology surrounding them. Functionally related to the basal ganglia but really located in the midbrain The largest nucleus of the midbrain.
As well as from serotonin receptors acid also binds to dopamine. How to Recognize LSD LSD is usually sold in tablets or capsules but sometimes in liquid form.
 Effective Connectivity Changes In Lsd Induced Altered States Of Consciousness In Humans Pnas
Effective Connectivity Changes In Lsd Induced Altered States Of Consciousness In Humans Pnas
The results of serial biopsy samples of the cerebral cortex indicated that the changes of brain fatty acid composition began as early as 1 week after fish oil feeding and stabilized at 12 weeks.

Acid effects on brain. But the researchers also found that the seat of consciousness in the brain the part thats called our default mode receives less blood under the influence of LSD. This may include altered awareness of the surroundings perceptions and feelings as well as sensations and images that seem real though they are not. The ability to see this internal activity is likely.
Lysergic acid diethylamide LSD also known colloquially as acid is a hallucinogenic drug. Folic Acid and the Aging Brain The demographic group with the highest incidence of folate deficiency is the elderly. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that helps control your behavior and mood governs your senses and moderates your thoughts.
Some possible side effects of LSD include distorted perceptions anxiety depression flashbacks dilated pupils and elevated blood pressure. This study examined the effect of citric acid on endotoxin-induced oxidative stress of the brain and liver. The physical effects of LSD are unpredictable from person-to-person.
Generally folic acid is safe in small doses or a short amount of time. It has proven unsafe for individuals who take it in large quantities for an extended period of time. If taken in large quantities side effects can include.
Acid primarily affects the prefrontal cortex area of the brain which controls mood thinking reactions panic and perception. Clearly it is important to make sure you get enough omega-3 fatty acids to avoid some of these detrimental effects on brain function and development. Long-Term Effects of LSD LSD does not cause addiction a brain disorder characterized by compulsive drug-seeking behavior.
However regular acid use can lead to long-term health problems. Mice were challenged with a single intraperitoneal dose of lipopolysaccharide LPS. It is thought LSD causes its characteristic hallucinogenic effects via interaction with the serotonin receptors in the brain.
Effects Of Acid On The Brain By WhatGo - 521 AM Lysergic acid diethylamide LSD also known as acid is a psychedelic drug known for its psychological effects. Study the causes effects along with a few examples and understand the prevention measures. Visit BYJUS to learn more about it.
LSD is a mind-altering drug. Dilated pupils increased blood pressure and increased body temperature are typical. Citric acid was given orally at 1 2 or 4 gkg at time of endotoxin injection and mice were euthanized 4 h later.
One of the key factors in brain atrophy in older individuals is an increased level of oxidative stress and DNA damage caused by increased levels of homocysteine an amino acid that is regulated by the presence of adequate folic acid. Acidity Effects On Your Brain. Many users have visual or auditory hallucinations.
Summary Omega-3s are vital for normal brain. WIKIMEDIA BEN MILLS The psychedelic drug lysergic acid diethylamide LSD is known for its euphoric effects and for inducing long trips Now in two studies published last week one in Current Biology the other in Cell scientists have examined how LSD produces such diverse effects and why the drug takes so long to wear offThe results of both studies suggest that LSDs effects are. Effects typically include altered thoughts feelings and awareness of ones surroundings.
What are the Side Effects of Taking Folic Acid. For example repetitive LSD use can cause persistent psychosis. The default mode network is the resting portion of the brain which is most active when the brain is at rest.
While people are on acid they start to see activity going on in the brain which is normally suppressed from perception Tagliazucchi explains. The main causes of acid rain are gases called sulfur dioxide SO2 and nitrogen oxides NOx. According to a 2016 study LSD also causes changes in the brains blood flow and electrical activity.
The same study also suggests it increases areas of communication in the brain. Acid Rain - Rain is called Acid Rain only if it has more acid than normal.
These arteries form a circle known as Willis circle which is named after Thomas Willis the British physician who discovered it. Arteries of the brain.
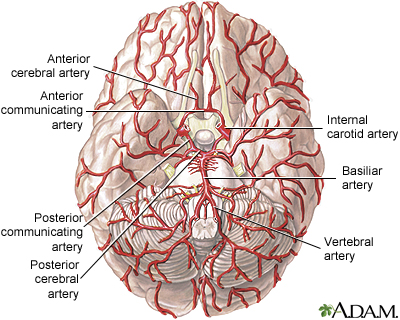 Arteries Of The Brain Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
Arteries Of The Brain Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
From this circle other arteriesthe anterior cerebral artery ACA the middle cerebral artery MCA the posterior cerebral artery PCAarise and travel to all parts of the brain.
Arteries of the brain. 9 minutes About fifteen percent 15 of the daily cardiac output is utilized by the brainOwing to the high oxygen and nutrient demand of the organ it is supplied by two arterial systems. The largest artery is the aorta the main high-pressure pipeline connected to the hearts left ventricle. 2 vertebral arteries and 2 internal carotid arteries.
This process is called atherosclerosis. The Arteries of the Brain Since the mode of distribution of the vessels of the brain has an important bearing upon a considerable number of the pathological lesions which may occur in this part of the nervous system it is important to consider a little more in detail the manner in which the vessels are distributed. The internal carotids and the vertebral arteries are the main vessels of the brain that supply blood to the brain.
The subclavian artery is divided into three parts based on anatomical landmarks. Anterior cerebral artery ACA Middle cerebral artery MCA Posterior cerebral artery PCA Both the ACA and MCA originate from the cerebral portion of internal carotid artery while PCA branches from the intersection of the posterior communicating artery and the anterior portion of the basilar artery. A brain AVM disrupts this vital process.
The internal carotid arteries and the vertebral arteries supply blood to the brain. The blood supply to the brain is via the internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries. Dimitrios Mytilinaios MD PhD Last reviewed.
Our vertebral arteries are located within the lateral spines of the neck or cervical spine thus being positioned along the course of the cervical vertebrae. Shelat DO FACP FAAN Attending Neurologist and Assistant Professor of Clinical Neurology Renaissance School of Medicine at Stony Brook University Stony Brook NY. Stroke A blood clot thrombus may form inside a brain artery that has been narrowed by atherosclerosis.
Currently about 75 of strokes in industrialized countries are thrombotic strokes. Carotid artery disease is caused by a buildup of plaques in arteries that deliver blood to your brain. The arteries are responsible for taking oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the brain.
The first part extends from its origin to the medial border of the scalenus anterior muscle. The derivatives of the internal carotid arteries form the anterior blood supply anterior circulation of the brain which includes the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. At the base of the brain the carotid and vertebrobasilar arteries form a circle of communicating arteries known as the Circle of Willis.
There are two paired arteries which are responsible for the blood supply to the brain. Review Date 6232020 Updated by. Within the cranial vault the terminal branches of these arteries form an anastomotic circle called the Circle of Willis.
Veins carry the oxygen-depleted blood back to the lungs and heart. Once this thrombus forms it cuts off the blood supply to part of the brain causing a thrombotic stroke. This vessel supports the anterior Circle of Willis.
The internal carotid artery and its branches make up the anterior circulation of the brain via the anterior and middle cerebral arteries whereas the vertebrobasilar arteries make up the posterior circulation of the brain via the posterior cerebral arteries. It is one of the largest blood suppliers to the cerebellum. The anterior cerebral artery forms the anterolateral portion of the circle of Willis while the middle cerebral artery does not contribute to the circle.
The three trunks which together supply each cerebral hemisphere arise from the arterial circle of Willis. These arteries arise in the neck and ascend to the cranium. Willis circle is located at the base of the brain where it is joined by other vessels of the brain.
The right and left posterior cerebral arteries arise from the basilar artery which is formed by the left and right vertebral arteries. Arterial Supply of Other Parts of the Brain The blood supply to the brain is supplied by 4 arteries. CAA increases the risk for stroke caused by bleeding and dementia.
This vessel is the largest in the vertebrobasilar system. An arteriovenous malformation can develop anywhere in your body but occurs most often in the brain or spine. The three main arteries are the.
Plaques are clumps of cholesterol calcium fibrous tissue and other cellular debris that gather at microscopic injury sites within the artery. The Basilar Artery is part of the vertebrobasilar system and is one the the major arteries in the brain. The vertebral arteries and the internal carotid arteries.
The aorta branches into a network of smaller arteries that extend throughout the body. The parts of the brain included within this arterial circle are the lamina terminalis the optic chiasma the infundibulum the tuber cinereum the corpora mammillaria and the posterior perforated substance. Vertebral arteries account for 30 of the blood supply to the brain supplying predominantly the posterior parts of the brain.
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy CAA is a condition in which proteins called amyloid build up on the walls of the arteries in the brain. Lorenzo Crumbie MBBS BSc Reviewer. November 13 2020 Reading time.
The vertebral arteries arise from the subclavian arteries. Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery.
These episodes can come and go and are a normal part of the recovery period. Brain tumors can create gaps in vision as well as weakness on one side of the body.
 Problem Side Effects After Brain Tumor Surgery
Problem Side Effects After Brain Tumor Surgery
Other people have some problems or long term difficulties.

Brain tumour surgery after effects. Most benign brain tumors are treatable with surgery. The problems you may have depends on the area of the brain where the tumour was or still is if you only had part of the tumour removed. You may also feel tired or weak.
They can affect different parts of the brain which control different functions. Find out more about what to expect when you first wake up and temporary short-term side-effects of neurosurgery. Things normalize after a few months and Ive got to admit.
The time it takes to heal after surgery is different for everyone. Some people who have had a brain tumour can develop side effects of treatment months or years later such as. Once the neurosurgery is over it will take time for you to regain your original level of energy.
Symptoms suggesting an intracranial bleed include a headache nausea and vomiting and neurological changes such as increasing weakness or numbness. This increases the pressure inside the skull and can make your symptoms worse for a short time. Other less common problems may occur after surgery for a brain tumor.
The surgical removal of a brain tumor whether malignant or benign also has a possible after-effect of bleeding. After Brain Tumor Surgery Before Treatment Brain surgery is a lot for the body to handle and you will likely experience some side effects as you recover. Side effects of treatment.
Cognitive functions such as reasoning thinking planning and organisation are most commonly affected each person in a different way and different severity. This is one of the cooler after-effects of brain surgery. The following information may provide peace of mind for patients and their caregivers.
Extreme care and recovery is mandatory after any brain tumor surgery to ensure your overall well being. Steroids can reduce swelling and pressure around the brain. For some reason I have struggling with the side effects in my head over the last few weeks.
Most challenging though was the cognitive loss that resulted from the first brain surgery which ultimately cost Smith his job. How much time to recover. Today after nine months of radiation and chemotherapy and 11 years later I am 51 years old and am living proof that there is life after being diagnosed with a malignant brain tumor.
Brain surgery is a lot for your body to cope with. The After Effects of Brain Surgery. The surgeon will access and remove all or part of your tumor depending on what can be safely accomplished.
Going home after brain tumour surgery. I am sure cold weather and being in a cold wind makes everything in my head tighten up and feel number again. Side-effects of a brain tumour Brain tumours may cause effects that can have an impact on your quality of life.
You may experience dizzy spells or get confused about where you are and whats happening. Some people wake up quickly after neurosurgery while others may take a few hours or days. Some people recover well after brain surgery but this can take some time.
Surgery to treat tumors that affect a certain part of the left frontal lobe can potentially damage Brocas area the language center of the brain and lead to difficulties with speech. I was at a factory so youre trying to keep pace with a machine that is kicking paper out really fast. Swelling in the brain after an operation means it will take some time before you feel the benefit from having your tumor removed.
Problems with thinking memory language or judgement. This means that the effects of a brain tumour you may experience depends on the location its size and its aggressiveness. You aint gonna poop for like a week.
Your caregiver may also experience stress difficulty sleeping anxiety and other indirect symptoms. Surgical resection of your tumor occurs in a hospital setting while you are under general anesthesia. The lower intestine is the last thing to wake up after major surgery.
A deeper look at the potential side effects of brain surgery such as bleeding seizure infections and strokes and how it can affect overall recovery. After surgery your team can adjust the plan if you need more relief. After neurosurgery Immediate effects.
You will probably spend a few days in the hospital. Surgery can cause swelling in the brain. You might need to have steroids after surgery either as tablets or injections.
One of the most common after effects of brain surgery and indeed in brain tumour sufferers is fatigue that affect all abilities that are essential for living our daily lives. Going home after brain tumour surgery can also be a nervous time. The brain may swell or fluid may build up within the skull.
Tumors at the cranial base usually involve the nerves of the face eyes ears and throat. 29 th December 2017. Plenty of rest is needed to provide adequate healing time for the brain tissues.
A tumour developing somewhere else. Injury to these nerves could cause double vision face weakness hearing. Long term problems after brain surgery.