In some cases transitional cell cancer metastasizes which means that. Cancer in this location is rare.

In upper urinary tract cancer abnormal cells are found in the.
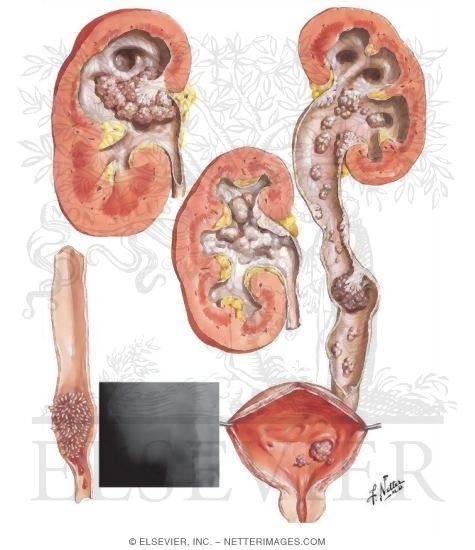
Cancer of the ureter. There are two kidneys one on each side of the backbone above the waist. In this module will introduce some basic information about kidney and ureter cancer. Other types of urethral cancer include.
It is also known as ureter cancer renal pelvic cancer and rarely ureteric cancer or uretal cancer. Ureteral cancer is uncommon. The extent of your surgery will depend on your situation.
Generally the earlier it is diagnosed and treated the better the outcome. The stages of ureter cancer are determined by the size of the malignancy and whether or not the cancer cells have spread past the ureter or renal pelvis. Urethral cancer is a disease in which malignant cancer cells form in the tissues of the urethra the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the bodyIt is a rare cancer that occurs more often in women than in men.
Statistics show that this kind of cancer is uncommon. Urethral cancer affects the tube that carries urine from your bladder to outside your body. The most common symptoms of ureter and renal pelvis cancer are blood in the urine pee called haematuria and pain in one side of the lower back.
Ureteral cancer treatment typically involves surgery. The 5-year survival rate is the percentage of people who are alive at least 5 years after their cancer diagnosis. The incidence rises from the age of 65 years and is even rarer under this age.
Higher incidence in men than women. Cancer that begins in the transitional cells is the most common type of cancer that develops in the renal pelvis and ureter. It is a part of the urinary tract which chiefly functions by carrying the urine produced by the kidneys to the bladder.
Low-grade cancers of the renal pelvis or ureter do not usually grow into the muscle layer of the renal pelvis or ureter wall and do not usually spread to other parts of the body. Your treatment options for cancer of the ureter will vary depending on the size and location of your cancer how aggressive the cells are and your own goals and preferences. Statistics related to kidney and ureter cancer different types of kidney and ureter cancers risk factors anatomy of the kidneys and ureters abstracting coding staging and treatment of kidney and ureter cancer.
But people with this type of cancer may live much longer than 5 years. The ureter is a long tube that connects the kidney to the bladder. Transitional cell carcinoma is a common cause of ureter cancer and other urinary tract cancers.
Ureteral cancer is cancer of the ureters muscular tubes that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Ureteral cancer is usually transitional cell carcinoma. It is quite rare in nature and is related to bladder cancer.
Localized cancer remains at the point of origin and has not spread beyond the kidney or ureter. High-grade cancers have a greater risk of spreading and a poorer prognosis. This is called hydronephrosis.
Ureteral cancer is the abnormal growth of cells that make up the inside of the tube that aids movement of urine from the kidney to the bladder. For tumors of the right renal pelvis the primary metastatic sites are the right renal hilar paracaval and retrocaval nodes. Upper tract urothelial carcinoma is a cancer that can occur anywhere from the inner linings of the kidney down the ureter in the bladder and down the urethra.
Cancer of the ureter ureteral cancer is an abnormal growth of cells on the inside lining of the tubes ureters that connect your kidneys to your bladder. Ureteral cancer is mostly diagnosed in people between the ages of 70 to 80 years. Surgery is often recommended to remove ureteral cancer.
They are considered bladder cancers rather than kidney cancers. Because of this low-grade cancers tend to have a good prognosis. Ureteral Cancer can be defined as the proliferation of cancer cells in the cellular lining of the ureter the tubes that connects the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
Regional cancer has progressed into the tissue surrounding the kidney andor neighboring lymph nodes while metastatic cancer has invaded other parts of the body. Symptoms may include a lump in the groin and difficulty peeing. Urethral cancer facts by John P.
Cancer of the renal pelvis small area in the centre of the kidney that the ureter arises from and ureter are very rare. Ureters are part of the urinary tract and they carry urine produced by the kidneys to the bladder. This causes urine to stay in the kidney and ureter.
Types of Ureter Cancer. Tumors of the upper two thirds of the right ureter primarily metastasize to the retrocaval and interaortocaval nodes. Sometimes the ureter may become blocked either by cancer cells or by a blood clot.
Tumors of the left renal pelvis metastasize to the left renal hilar and para-aortic nodes. Transitional cell cancer of the renal pelvis and ureter is a disease in which malignant cancer cells form in the renal pelvis and ureter. Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type of urethral cancer.
Transitional cell carcinoma is a form of ureter cancer that usually develops in the prostate in men and around the opening of the urethra in women. The most common type of cancer that affects the ureter is squamous cell carcinoma which affects surface cells by the bladder in women and in the penis in men. Cancer of the renal pelvis or ureter is often found at an early stage.
The renal pelvis is the top part of the ureter. Cancer of the ureter. Kidney Ureter Cancer.
Cancer is when cells in the body grow out of control often forming a mass or tumor. Renal pelvis where urine collects in the kidneys before it travels to the ureters and bladder Renal calyces spaces deep in the kidneys.