The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus theorem that shows the relationship between the concept of derivation and integration also between the definite integral and the indefinite integral consists of 2 parts the first of which the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 1 and second is the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 2. After tireless efforts by mathematicians for approximately 500 years new techniques emerged that provided scientists with the necessary tools to explain many phenomena.
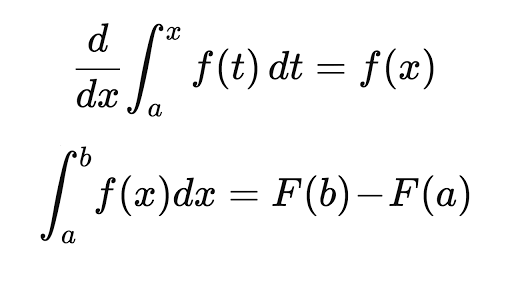
State the meaning of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 2.

Fundamental theorem of calculus part 2. The fundamental theorem of calculus is a theorem that links the concept of differentiating a function with the concept of integrating a function. A b f x d x F b F a. Thanks to all of you who support me on Patreon.
If f is continuous on a b and F x f x then a b f x d x F b F a. Well we could denote that as the definite integral between a and b of f of t dt. Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part Two textTheoremspace boxedint _ a b fprime left x right dx fleft b right -fleft a rightquad textAssumingspace fprime left x right space textis continuous.
In contrast to the indefinite integral the result of a definite integral will be a number instead of a function. The Fundamental Theorem of. Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 2.
The Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Then Fx fx at each point in I. The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 2 is perhaps the most important theorem in calculus.
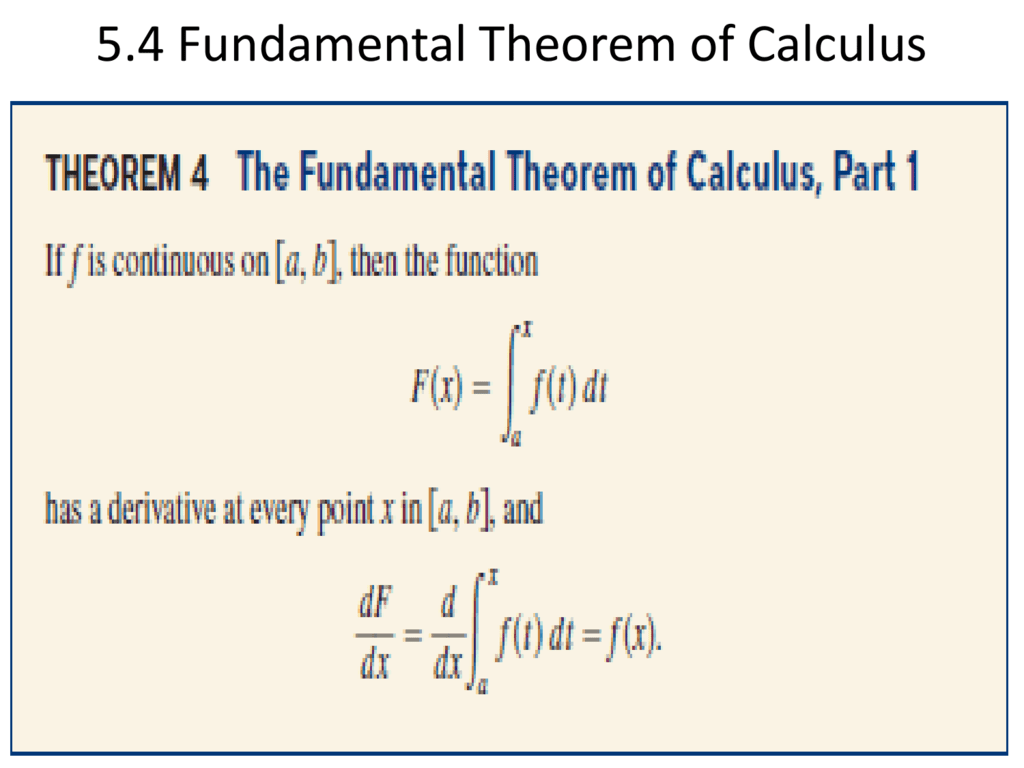
The first part of the theorem sometimes called the first fundamental theorem of calculus states that one of the antiderivatives say F of some function f may be obtained as the integral of f with a variable bound of integration. Part 1 of Fundamental theorem creates a link between differentiation and integration. How to Calculate Definite.
Here the Fx is a derivative function of Fx. You must add a full line of space before and after lists for them. The result of Preview Activity 52 is not particular to the function f t 4 2t nor to the choice of 1 as the lower bound in the integral that defines the function A.
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. So the second part of the fundamental theorem says that if we take a function F first differentiate it and then integrate the result we arrive back at the original function but in the form F b F a. Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 2.
Explain the relationship between differentiation and integration. You da real mvps. Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus We have learned about indefinite integrals which was the process of finding the antiderivative of a function.
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 2 FTC 2 relates a definite integral of a function to the net change in its antiderivative. Part 2 Let fx be continuous in the domain ab and let Fx be any antiderivative of fx ie where Fxfx then. And there you have it.
If f is continuous on a b and F x f x then. The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part II goes like this. 1 per month helps.
Suppose Fx is an antiderivative of f x. Use the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 2 to evaluate definite integrals. This gives us an incredibly powerful way to compute definite.
Second Fundamental Theorem of Integral Calculus Part 2 The second fundamental theorem of calculus states that if a function f is continuous on an open interval I and a is any point in I and the function F is defined by. This implies the existence of antiderivatives for continuous functions. It tells us that if f is continuous on the interval that this is going to be equal to the antiderivative or an antiderivative of f.
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 1. Thus the two parts of the fundamental theorem of calculus say that differentiation and integration are inverse processes. Conversely the second part of the theorem someti.
This right over here is the second fundamental theorem of calculus. There are really two versions of the fundamental theorem of calculus and we go through the connection here. If a function is continuous on an interval then it follows that where is a function such that is any antiderivative of.
By that the first fundamental. This FTC 2 can be written in a way that clearly shows the derivative and antiderivative relationship as. Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 2.
A b g x d x g b g a. Int_ab fxdx quad quad Fb-Fa. Created by Sal KhanPractice this lesson yoursel.
In the previous two sections we looked at the definite integral and its relationship to the area under the curve of a function. Theorem 1 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 2.
Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Calculus 1 Overview Study Guide
 5 4 Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Part 2 Tutorial Sophia Learning
5 4 Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Part 2 Tutorial Sophia Learning
 Using The Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus To Show Antiderivatives Study Com
Using The Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus To Show Antiderivatives Study Com
 The Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Part 1 2 Waterloo Standard
The Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Part 1 2 Waterloo Standard
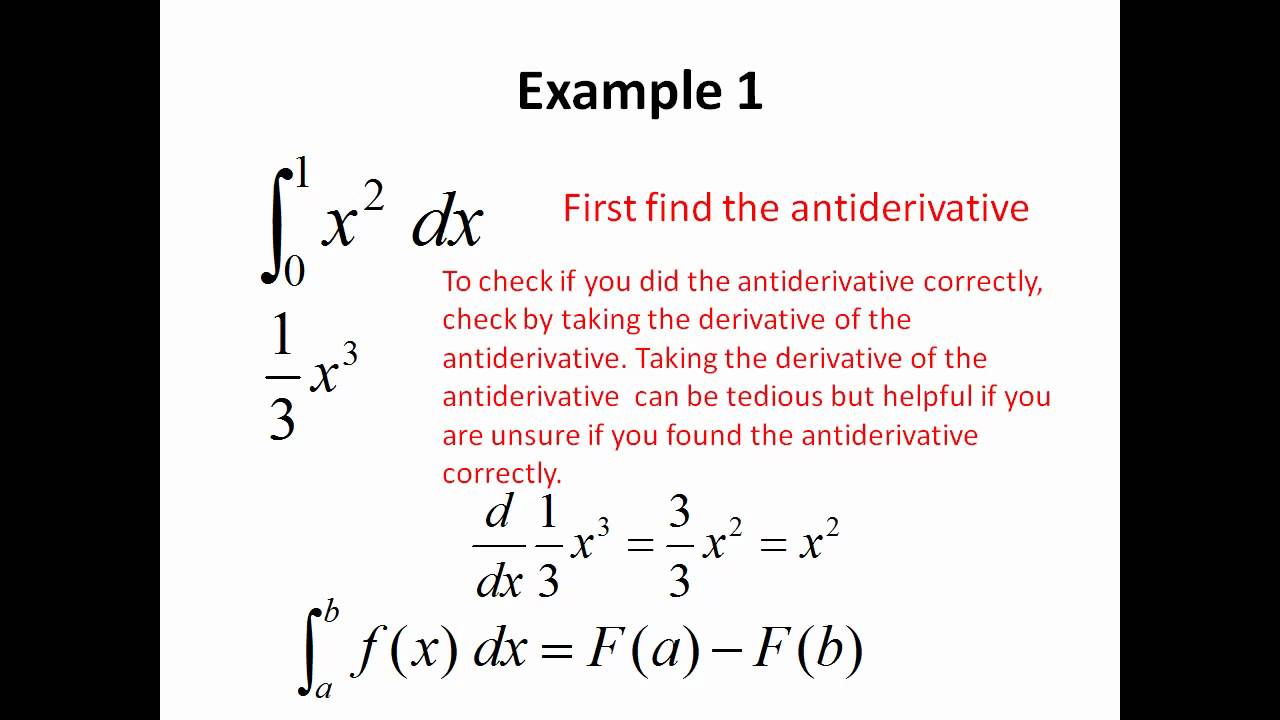 Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Part 2 Youtube
Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Part 2 Youtube
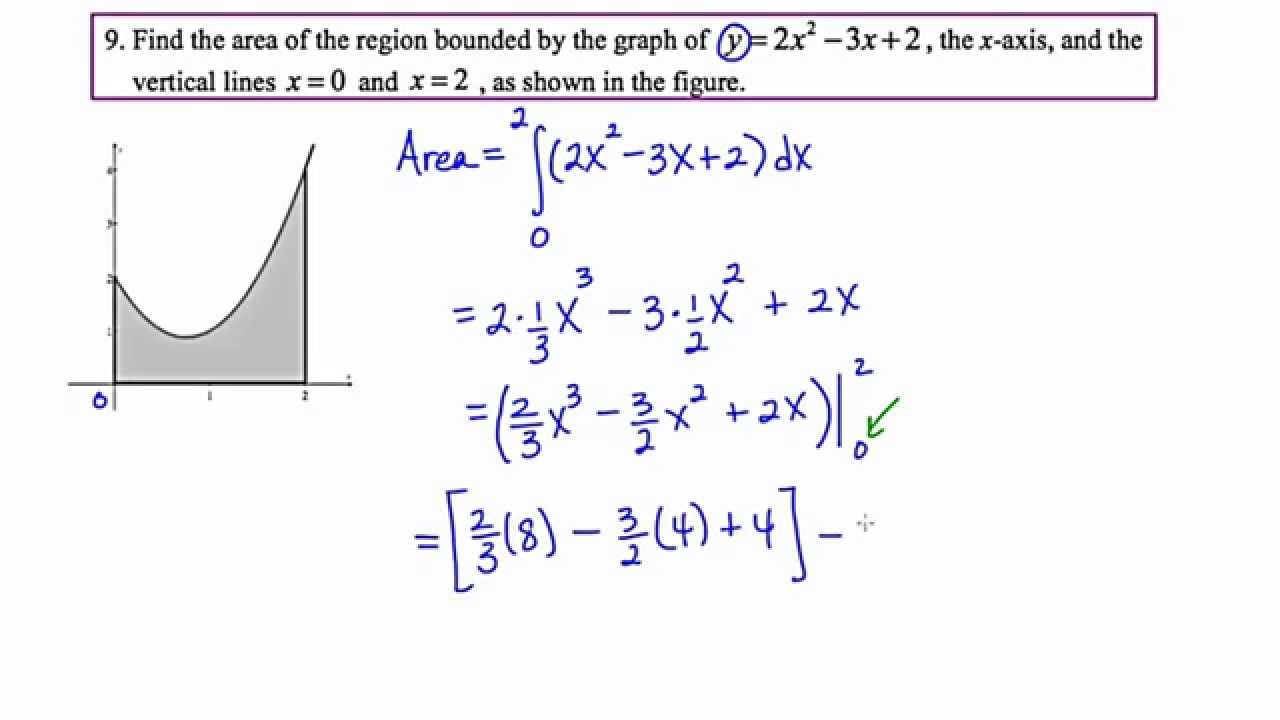 Mathcamp321 Calculus The Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Part 2 4 4 Youtube
Mathcamp321 Calculus The Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Part 2 4 4 Youtube
 Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Part I Mathematics Stack Exchange
Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Part I Mathematics Stack Exchange
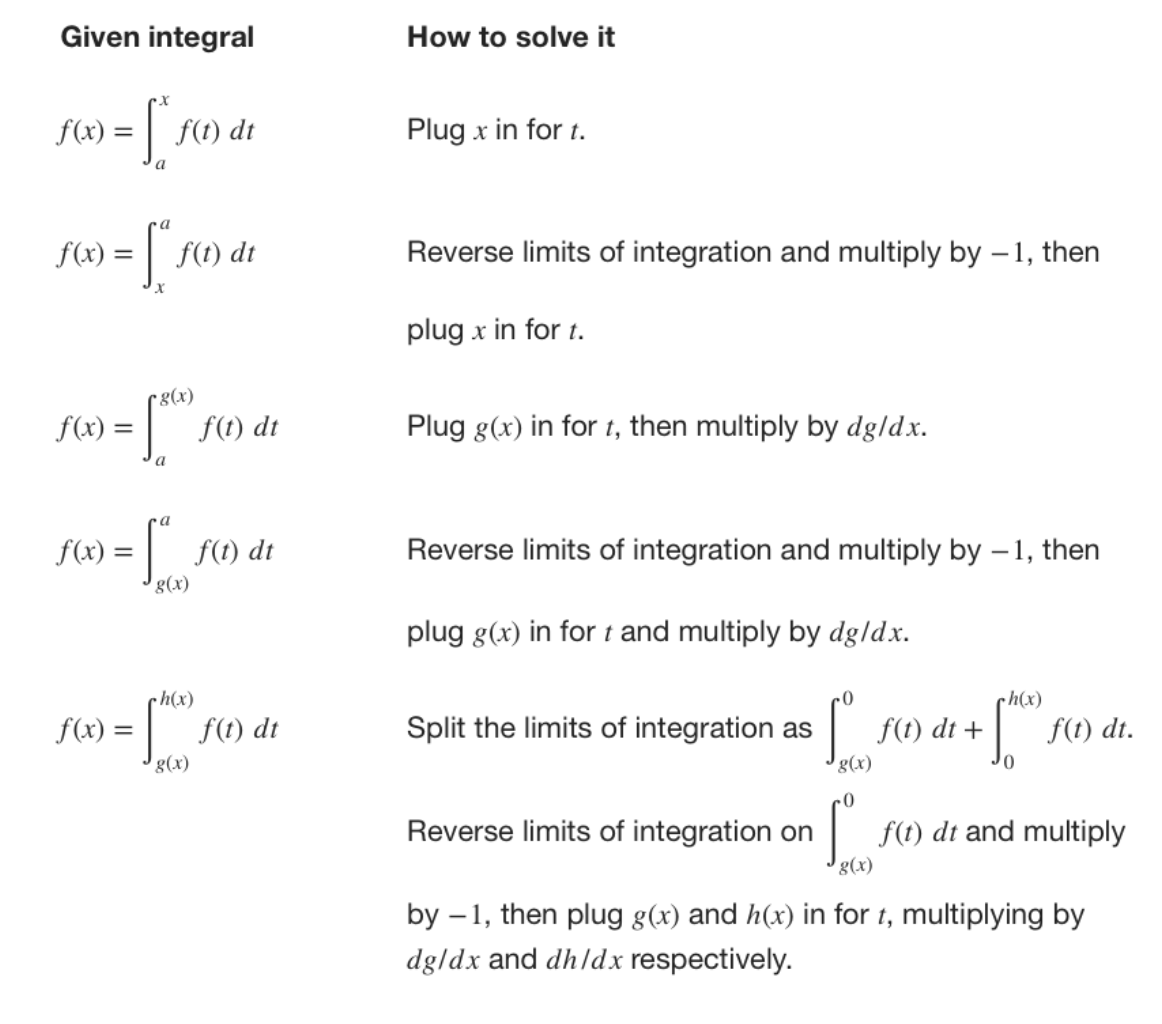
 Section 4 3 Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Math 1231 Single Variable Calculus Ppt Download
Section 4 3 Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Math 1231 Single Variable Calculus Ppt Download
 5 4 Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus
5 4 Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus
 Section 5 4a Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Deriving The Theorem Let Apply The Definition Of The Derivative Rule For Integrals Ppt Download
Section 5 4a Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Deriving The Theorem Let Apply The Definition Of The Derivative Rule For Integrals Ppt Download
 Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Part 2 Youtube
Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Part 2 Youtube
 Understanding The Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Mathematics Stack Exchange
Understanding The Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Mathematics Stack Exchange