Thyroid nodules can be detected in 4 to 8 of the adult population by palpation but in 40 to 50 of the population by ultrasound. Ultrasound uses soundwaves to create a picture of the structure of the thyroid gland and accurately identify and characterize nodules within the thyroid.
 Ultrasonographic Features For Differentiating Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma And Follicular Adenoma Sciencedirect
Ultrasonographic Features For Differentiating Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma And Follicular Adenoma Sciencedirect
Imaging techniques particularly high resolution sonography of the neck have been shown to.

Malignant thyroid nodule ultrasound. Malignancy prevalence in nodules with a highly suspicious ultrasound category based on ATA Criteria was 685 significantly higher than indeterminate nodules with low-risk ultrasound patterns per the ATA. 1 They are palpable in 47 of the population and have been detected using ultrasonography in up to 67 of adults. The ACR-TIRAD uses ultrasound data and a point system based on nodule composition echogenicity nodule fluid content shape nodule margins and echogenic foci particulates within the nodule of differing echogenicity 6-8.
Since thyroid nodules are frequently detected by cervical ultrasound examinations distinguishing between a benign and a malignant nodule is a relevant clinical challenge. Clinical Oncology Feb 21 2017. Thyroid nodules are commonly detected on physical examination and even more commonly identified as incidental findings on computed tomography CT magnetic resonance imaging MRI radionuclide studies and ultrasound examinations of the neck done for other purposes than evaluating the thyroid gland Fig.
Similar results were found when researchers stratified for papillary thyroid carcinoma and its variants. Ultrasound is the first-line imaging modality for assessment of thyroid nodules found on clinical examination or incidentally on another imaging modality. Suspiciously malignant findings on ultrasound after fine needle aspiration biopsy in a thyroid nodule with initially benign ultrasound and cytologic result.
The overwhelming majority of these represent benign hyperplastic nodules or adenomas. 2 While the majority of nodules are benign the risk of malignancy reaches approximately 715. Approximately 5 of nodules are malignant with papillary carcinoma representing approximately 75.
Ultrasound of Thyroid Nodules. Thyroid nodules are discrete lesions present within the thyroid gland that are radiologically distinct from the adjacent parenchyma Table 1. Zhang eet al Int J.
A few Radiomics studies have been conducted on ultrasound images for classifying benign and malignant thyroid nodules 91821. To repeat or to follow-up Clinical Imaging Vol. A simple procedure that is done in the doctors office to determine if a thyroid nodule is benign.
Partially cystic thyroid nodules on ultrasound. The total point value is divided into five levels with TR1 and TR2 being the lowest. Ultrasound USG can be a good screening tool to identify high-risk nodule requiring fine-needle aspiration cytology FNAC.
A cross-sectional study was performed from August 2011 to July 2012 at Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital. 1 Given the prevalence of thyroid nodules and their underlying risk it is imperative that general practitioners GPs are able to. Thyroid malignancy is relatively rare and is diagnosed in approximately 25000 patients per year in the United States 1.
Thyroid fine needle aspiration biopsy FNAB. Height of the nodule nodular calcifications ill defined nodule borders irregular shape were associated with a higher score for malignancy. Thyroid nodules are commonly noted in adults.
This article is an overview of ultrasonographic features of thyroid nodules which are used to determine the need for biopsy with fine needle aspiration. The prevalence of palpable thyroid nodules is estimated to be 64 in women and 15 in men between 30 to 60 years of age living in iodine-sufficient regions. The most common cause of benign thyroid nodules is nodular hyperplasia 2.
With respect to current guidelines it is the sonographic pattern rather than the growth of a nodule that raises suspicions of malignancy 15. Probability of malignancy and sonographic differentiation About 5 of partially cystic nodules in our series were malignant. A common imaging test used to evaluate the structure of the thyroid gland.
The study aimed to assess the association of USG characteristic of thyroid nodule with malignancy. When more than 50 of the nodule is solid and the solid portion of the nodule is eccentric the risk of malignancy is greater. Thyroid nodules are a common clinical finding and are increasingly detected in the general population due to the widespread use of thyroid ultrasound US examination 1 2Fine-needle aspiration FNA biopsy is currently the main diagnostic tool for the detection of the minority of thyroid lesions that result to be malignant 3 4Its use should be restricted to thyroid nodules associated.
Ultrasound can detect the presence site size and number of thyroid nodules and there have been reports of US characteristics of malignancy such as ill-defined margin irregular shape hypoechogenicity heterogeneity absence of cystic lesion andor the halo sign the presence of calcification and invasion to adjacent organs. Ultrasound is also frequently used to guide the needle into a nodule during a thyroid nodule biopsy. Also the study suggested a less than 2 cm under ultrasonography as the cutoff for malignancy.
Ultrasound can help evaluate a thyroid nodule and determine the need for biopsy. A thyroid fine needle aspiration biopsy can collect samples of cells from the nodule which under a microscope can provide your doctor with more information about the behavior of the nodule. What does a Malignant Thyroid Nodule Look Like on Ultrasound Imaging.
Therefore it is worthy of investigating whether a Radiomics approach can make better use of thyroid ultrasound images and achieve more accurate diagnosis of differentiating malignant from benign thyroid nodules. Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytopathology can predict oversize of thyroid nodule than original but may predict the risk of malignancy of the thyroid nodule. Whats the treatment for a thyroid nodule.
Thyroid nodules are very common and may be observed at ultrasonography US in 50 of the adult population.
 Thyroid Nodules Thyroid Cancer Ucla Endocrine Center Los Angeles Ca
Thyroid Nodules Thyroid Cancer Ucla Endocrine Center Los Angeles Ca
Thyroid Nodules Endocrinesurgery Net Au
 Multinodular Goiter And Solitary Nodule Endocrinology Advisor
Multinodular Goiter And Solitary Nodule Endocrinology Advisor
 Ajr Researchers Take Step Toward Automating Thyroid Cancer Triage Eurekalert Science News
Ajr Researchers Take Step Toward Automating Thyroid Cancer Triage Eurekalert Science News
 Using Artificial Intelligence To Predict Risk Of Thyroid Cancer On Ultrasound
Using Artificial Intelligence To Predict Risk Of Thyroid Cancer On Ultrasound
 Differentiation Of Benign And Malignant Thyroid Nodules By Using Comb Push Ultrasound Shear Elastography A Preliminary Two Plane View Study Sciencedirect
Differentiation Of Benign And Malignant Thyroid Nodules By Using Comb Push Ultrasound Shear Elastography A Preliminary Two Plane View Study Sciencedirect
 Usg Ultrasonography Ultrasonography 2288 5919 2288 5943 Korean Society Of Ultrasound In Medicine 10 14366 Usg 15016 Usg 15016 Original Article Differentiation Of Benign And Malignant Thyroid Nodules Based On The Proportion Of Sponge Like Areas
Usg Ultrasonography Ultrasonography 2288 5919 2288 5943 Korean Society Of Ultrasound In Medicine 10 14366 Usg 15016 Usg 15016 Original Article Differentiation Of Benign And Malignant Thyroid Nodules Based On The Proportion Of Sponge Like Areas
Ultrasound Based Diagnostic Classification For Solid And Partially Cystic Thyroid Nodules American Journal Of Neuroradiology
 Hot Thyroid Nodules Can Sometimes Be Cancer
Hot Thyroid Nodules Can Sometimes Be Cancer
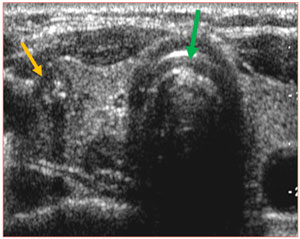 Diagnosis Of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Diagnosis Of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
 Thyroid Nodules Investigation And Follow Up Tidsskrift For Den Norske Legeforening
Thyroid Nodules Investigation And Follow Up Tidsskrift For Den Norske Legeforening
 Pattern Recognition Of Benign And Malignant Thyroid Nodules Ultrasound Characteristics And Ultrasound Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Of Thyroid Nodules Radiology Key
Pattern Recognition Of Benign And Malignant Thyroid Nodules Ultrasound Characteristics And Ultrasound Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Of Thyroid Nodules Radiology Key
How Do You Evaluate And Treat A Thyroid Nodule Pediatriceducation Org
